Cataracts are the world’s leading cause of blindness. On World Sight Day, learn what Sightsavers is doing to protect the sight of children with cataracts in Zambia.
First published in September, 2023, by Sightsavers. All images © Sightsavers/Hudson Chirwa.
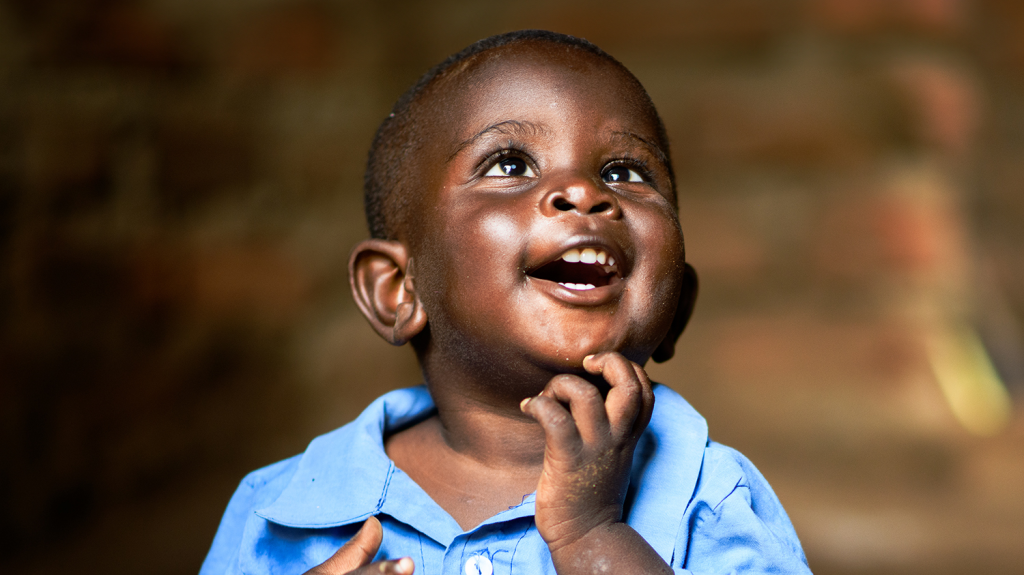

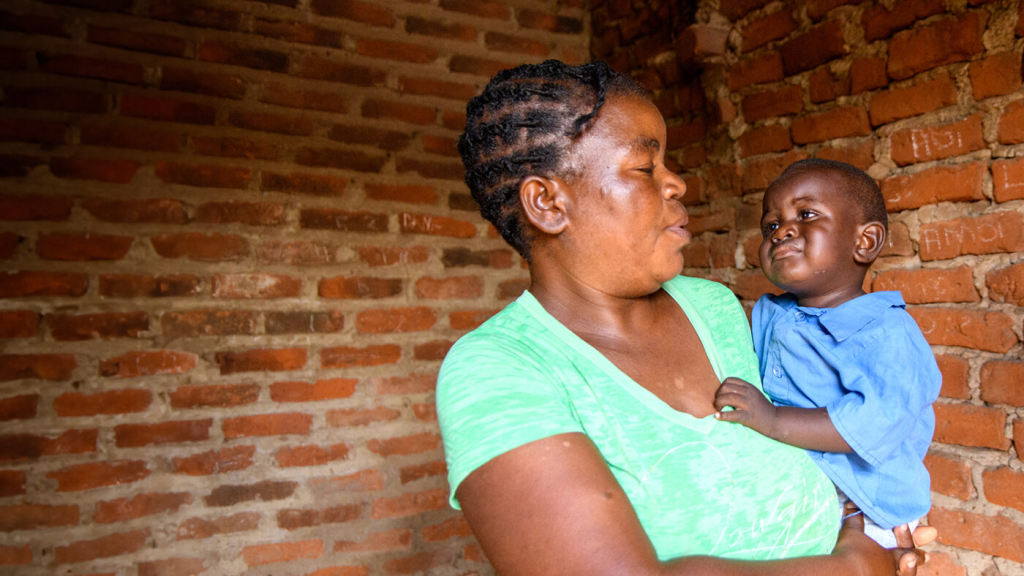
Mobwin is just one year old. His mother, Nsenga, explains how her son’s cataracts were diagnosed.
“We discovered he had some white dots in his eyes, so I took him to the hospital. But the problem persisted instead of getting better. I later received a call that they wanted to check his eyes again and that an [eye health] programme had begun. I was told he had cataracts.”
After operating on one of Mobwin’s eyes, Nsenga remarked on the change in her son. “We could hear Mobwin murmur and he started singing. He likes to sing. If we play gospel music, he will be happy. He makes me happy with his singing.”
Mobwin’s father, Undani, also saw the change in Mobwin. “Before, whenever you waved a hand across his eyes, he wouldn’t react, but now, when you do that, he sees and pushes it to the other side.
“I want my child to attain his education and learn how to write. I know he will have a bright future. I encourage other parents to take their children to the hospital.”

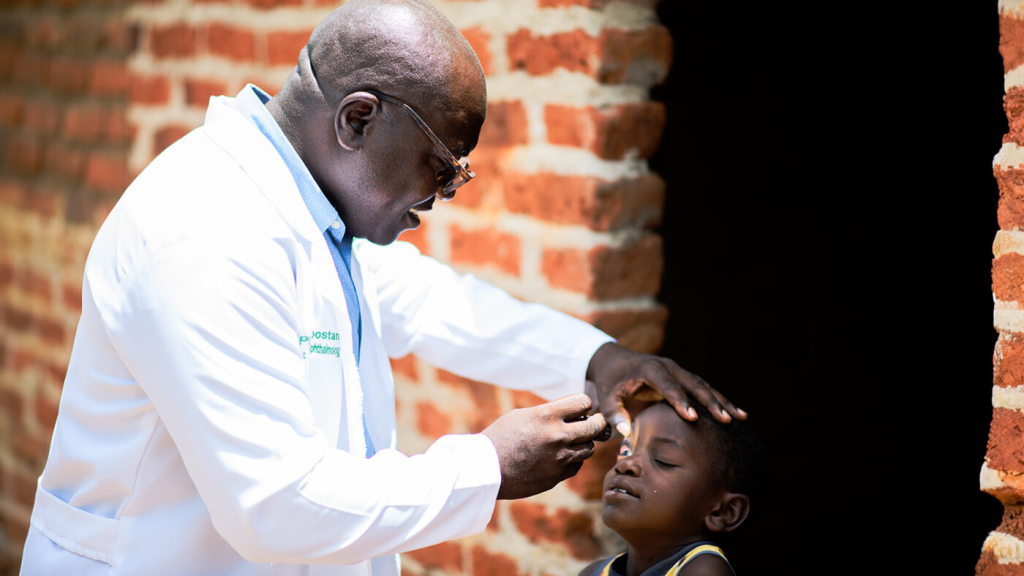
Children like Mobwin, who have vision problems, are treated by Mr Phiri, an ophthalmic doctor working in Zambia.
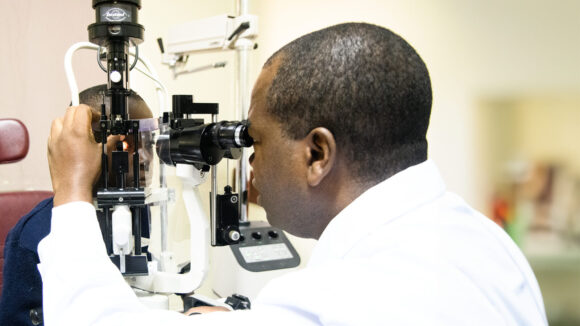
“I work at Petauke District Hospital in the eastern province, where I do cataract surgeries. I have a passion for eyes because there used to be no eye health staff working in this district. Because of this, I was sent to go and train in that field.
“For children, we have different types of cataracts. It can be congenital and they are born with it. Or it can develop from trauma such as being hit by stones or a ball. We call it ‘cataract extraction’: we remove the cataract within the lens, clean it with the drip and replace it with an artificial lens.
“The next day, we remove the bandage. For healing, we ask the patient to avoid difficult work and activities.”
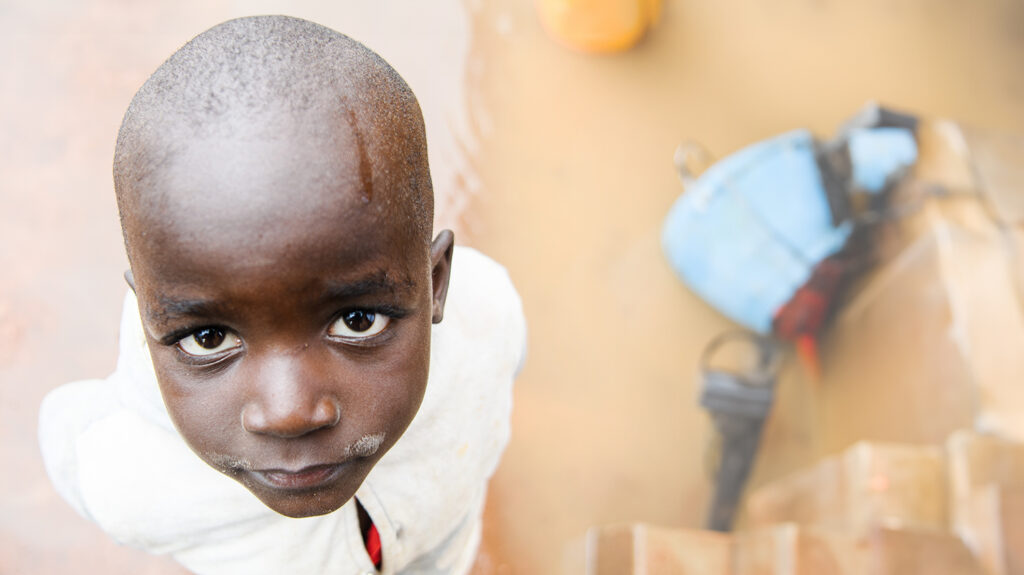
Another child who was able to be treated is 11-year-old Emmanuel. He loves fast sports cars and feels happiest when solving maths problems.

“When I am in class, it’s difficult for me to see clearly what is written on the board,” he says. “I can’t see from a distance, so I sit in front. I close one eye when playing because my eyes are so painful. My teacher said I should go to the hospital.”
Emmanuel’s family are familiar with childhood cataracts, as his mother, Gift, had them same eye condition when she was younger. “My performance at school was poor as I could not see properly,” she says. “I regained my sight after surgery, but it delayed me finishing my education. I’m now a teacher and I didn’t want Emmanuel to go through what I experienced.”
Gift is thankful that her son was able to have cataract surgery. “I am very happy seeing my son this way and the journey was a success. I know the future is going to be bright.”

Emmanuel and Mobwin’s operations were funded as part of Sightsavers’ inclusive eye health project. As well as carrying out eye operations, the project is sharing information about cataracts across the province.

Mr Phiri says: “There have been great improvements in the province. We go into the community and tell them how cataracts can develop. We have been meeting all the chiefs to show them the importance of cataracts. We have now trained more women than men as cataracts finders in the communities. They send a list to us, and we go check them.
“The distance is very far [to reach some communities]. It has been difficult, and we use motorbikes to go into the jungle, which is also risky. We also need security and are not well supported for the distant places we tackle.”

“We cannot say we are winning the fight because, as a human resource, we are few,” explains Mr Phiri. “There are some districts with no eye health provision. For example, Nyimba and Sinda have no trained personnel. We fight hard to reach where we are supposed to be.

We can’t do anything without our partners. We would be just screening without a map and giving prescriptions to people who can’t buy medication.
“My main message [to our donors] is for them to continue supporting people with sight problems. Thousands of people have been helped because of them. I would like to thank them for helping people. I am raising my hands and saying thank you to those people.”
